Bosch task¶
This document describes the task used to communicate with the bosch system, from now on called Bosch task. This task contains some public methods that must be used to send the required actions to the wanted bosch axis.
Task public methods¶
Here the methods for the Bosch task are explained.
InitSubsystem¶
Used to initialize the subsystem. Do it before starting the statechart, as part of the subsystem init actions. This method will be the only one that will wait until the task answers to keep going. The task could answer an error or nothing is everything goes fine.
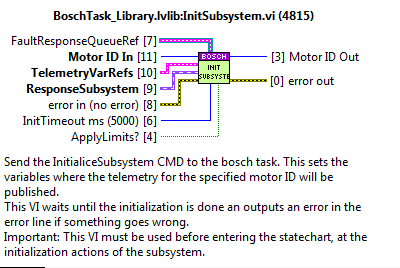
Inputs:
MotorID: the identifier of the motor. From this moment on, this ID will be the reference the data related to the subsystem/motor.
FaultResponseQueueRef: the queue used to publish the error info when a fault is triggered from the task. Saved in the task related to the motor ID.
TelemetryVarRefs: variables used to publish the telemetry of the system. Saved in the task related to the motor ID. If the variable is left empty nothing will be published for that topic.
TrackActive? var ref. Boolean type var.
Position var ref. DBL array type var.
Velocity var ref. DBL array type var.
Status var ref. String type var.
Status code var ref. I32 type var.
Torque var ref. DBL array type var.
Acceleration var ref. DBL array type var.
Positive limit: Limit.ctl
LimitVar2Publish Boolean type var.
Negate?
Bit
Negative limit: Limit.ctl
LimitVar2Publish Boolean type var.
Negate?
bit
ResponseSubsystem: an input of the SubsystemGeneral.lvclass, is used to have the dynamic dispatch to the actual subsystem. Saved in the task related to the motor ID.
Error In: transmits the error.
InitTimeout ms: this is the timeout of the CMD, if this timeout is exceeded the subsystem did not start well and an error is triggered.
Apply limits?: this is to tell the system that has to check for the limits of the subsystem or not.
CloseTask¶
Method to close the app.
ExitSubsystem¶
Method to exit a subsystem, this means closing the related refs.
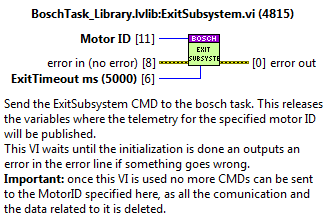
Inputs:
MotorID: the identifier of the motor. The reference to the data related to the subsystem/motor.
ExitTimeout ms: this is the timeout of the CMD, if this timeout is exceeded the subsystem did not stop well and an error is triggered.
Get Axis Info¶
Returns the position and speed. The values are taken from FGV_AxisInfo.
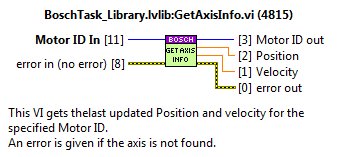
Inputs:
MotorID: the identifier of the motor. The reference to the data related to the subsystem/motor.
Move¶
Used for a Move CMD.
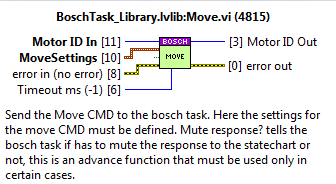
Inputs:
MotorID: the identifier of the motor.
Timeout ms: the timeout value for the CMD. If not wired the default value is -1, this means that timeout is not applied.
Settings: MotionMoveAbsolute.ctl from MLPI
Position
Velocity
Acceleration
Deceleration
Jerk
MuteResponse?: used to mute the answer to the statechart.
MoveVelocity¶
Used for a MoveVelocity CMD.
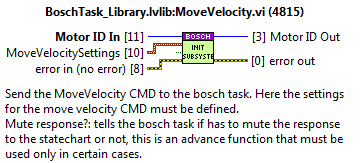
Inputs:
MotorID: the identifier of the motor.
Settings: MotionMoveVelocity.ctl from MLPI
Velocity
Acceleration
Deceleration
Jerk
MuteResponse?: used to mute the answer to the statechart.
Power¶
Used for a Power CMD.
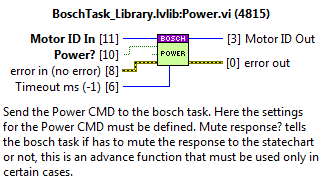
Inputs:
MotorID: the identifier of the motor.
Timeout ms: the timeout value for the CMD. If not wired the default value is -1, this means that timeout is not applied.
Settings:
Power?: Tells the bosch task if has to turn on the axis or turn it off.
MuteResponse?: used to mute the answer to the statechart.
GetAxisStatus¶
Obtain the status of a specified Axis. Alberto thinks it’s interesting to know the status if the axis is in fault or in parking.
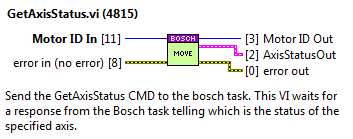
Inputs
MotorID: the identifier of the motor.
Reset¶
Used for the Reset CMD.
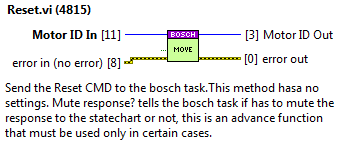
Inputs:
MotorID: the identifier of the motor.
MuteResponse?: used to mute the answer to the statechart.
Stop¶
Used for the Stop CMD.
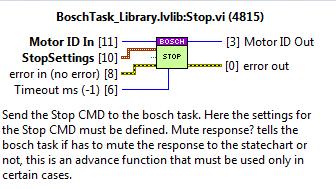
Inputs:
MotorID: the identifier of the motor.
Timeout ms: the timeout value for the CMD. If not wired the default value is -1, this means that timeout is not applied.
Parameters: StopSettings_TypeDef.ctl
Deceleration
Jerk
MuteResponse?: used to mute the answer to the statechart.
Track¶
Used for the Track CMD. The Bosch task does no longer have the tracking inside, the track CMD available just sends the move continuous when received to the specified axis.
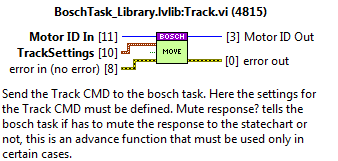
Inputs:
MotorID: the identifier of the motor.
Parameters:
Parameters: MoveContinuousAbsolute
Position
endVelocity
Velocity
Acceleration
Deceleration
Jerk
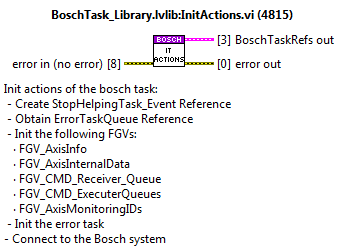
Init and Exit Actions¶
Init actions¶
Init actions of the bosch task:
Create StopHelpingTask_Event Reference
Obtain ErrorTaskQueue Reference
Init the following FGVs:
FGV_AxisInfo
FGV_AxisInternalData
FGV_CMD_Receiver_Queue
FGV_CMD_ExecuterQueues
FGV_AxisMonitoringIDsInit needed queues and DVRs
Init the error task
Send Connect to the PLC
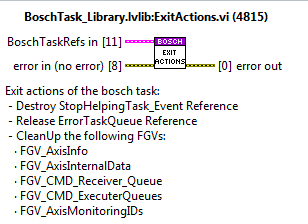
Exit actions¶
Exit actions of the bosch task:
Destroy StopHelpingTask_Event Reference
Release ErrorTaskQueue Reference
CleanUp the following FGVs:
FGV_AxisInfo
FGV_AxisInternalData
FGV_CMD_Receiver_Queue
FGV_CMD_ExecuterQueues
FGV_AxisMonitoringIDs
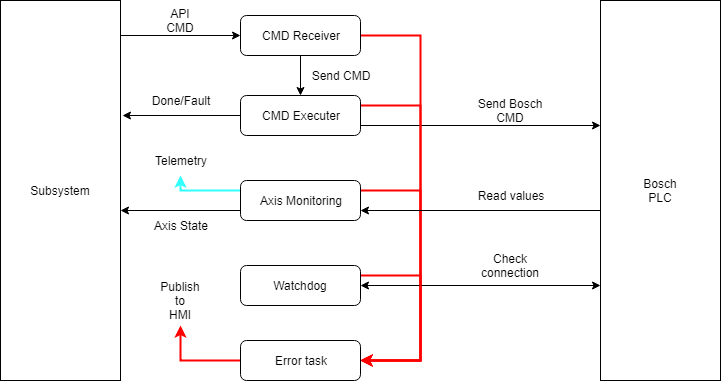
Task loops¶
The bosch task has 5 tasks inside that manage different parts needed to operate the bosch system, each of them is explained in the upcoming sections.
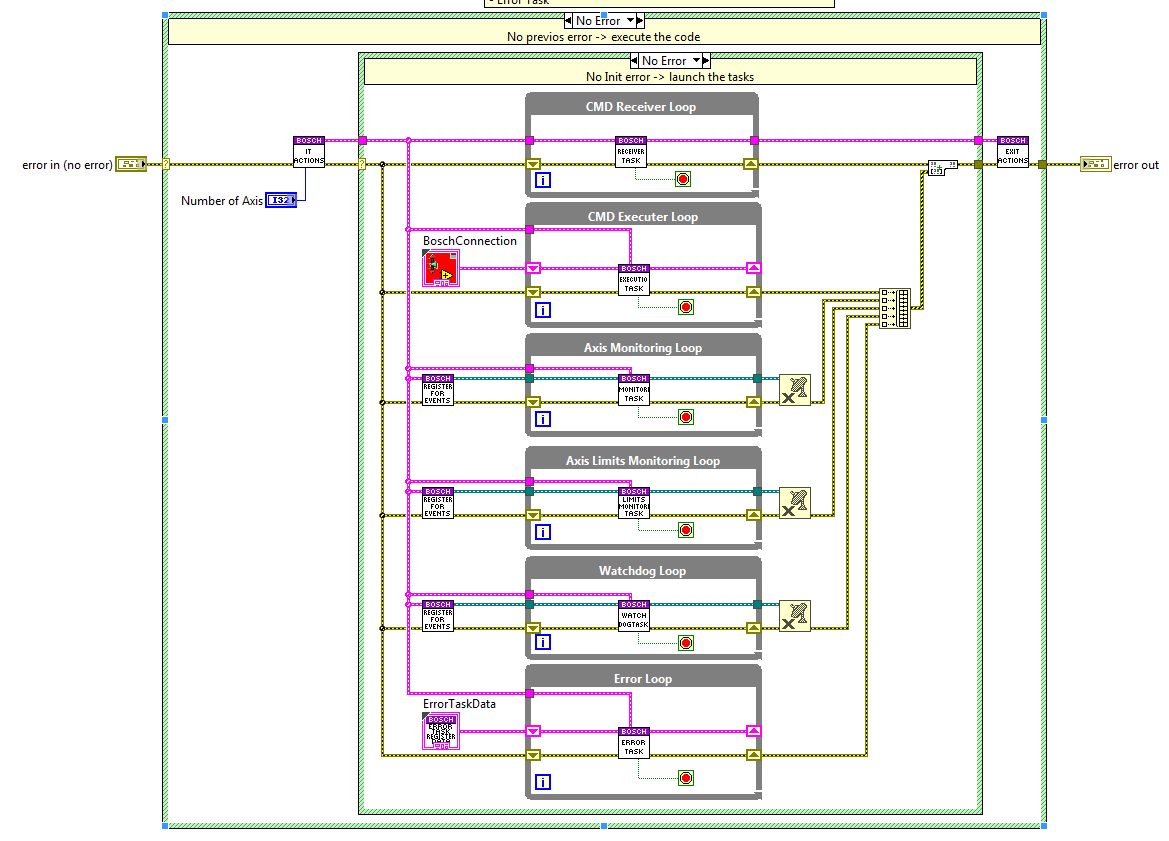
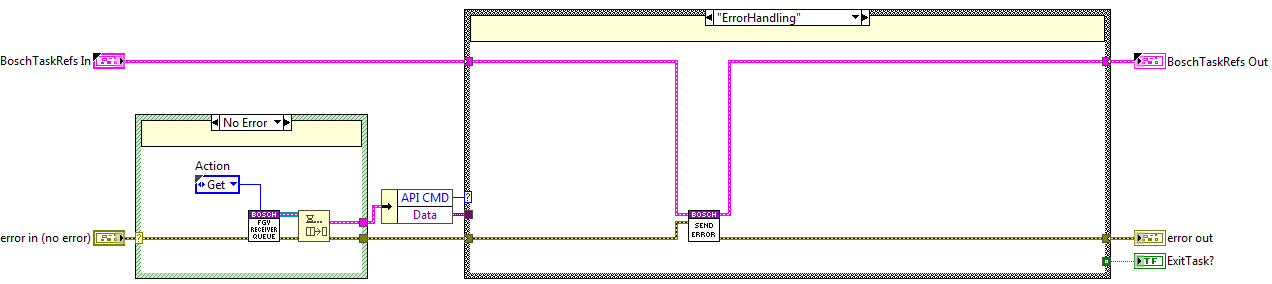
CMD Receiver loop¶
This loop receives the CMDs from the API and executes the required actions for each CMD.
Task communication¶
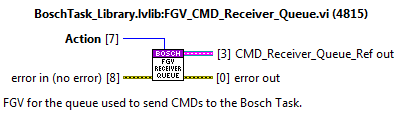
The communication between the methods and the task is very simple and is done using a queue. This queue is initialized at the init actions of the bosch task and released at the exit actions. The reference of the queue is saved to a FGV, this FGV is called: “FGV_CMD_Receiver_Queue.vi” see figure below.
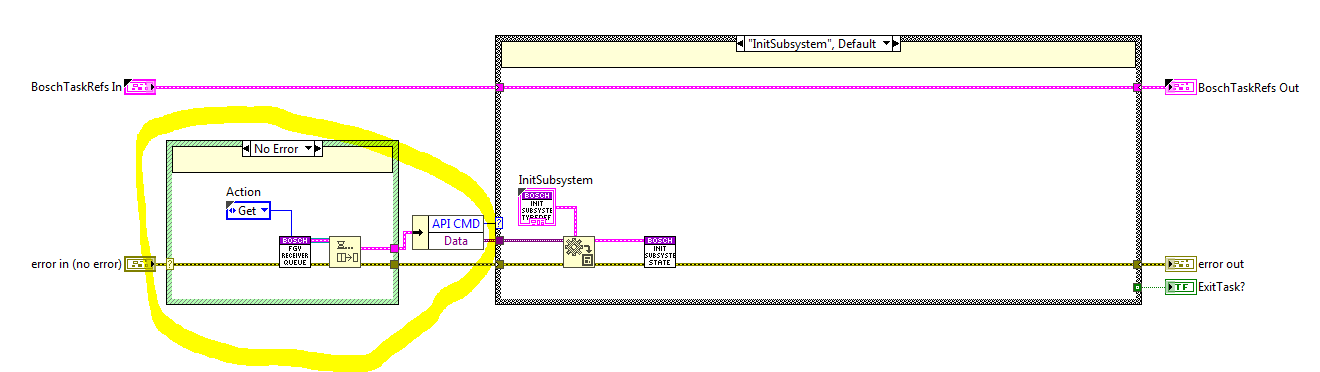
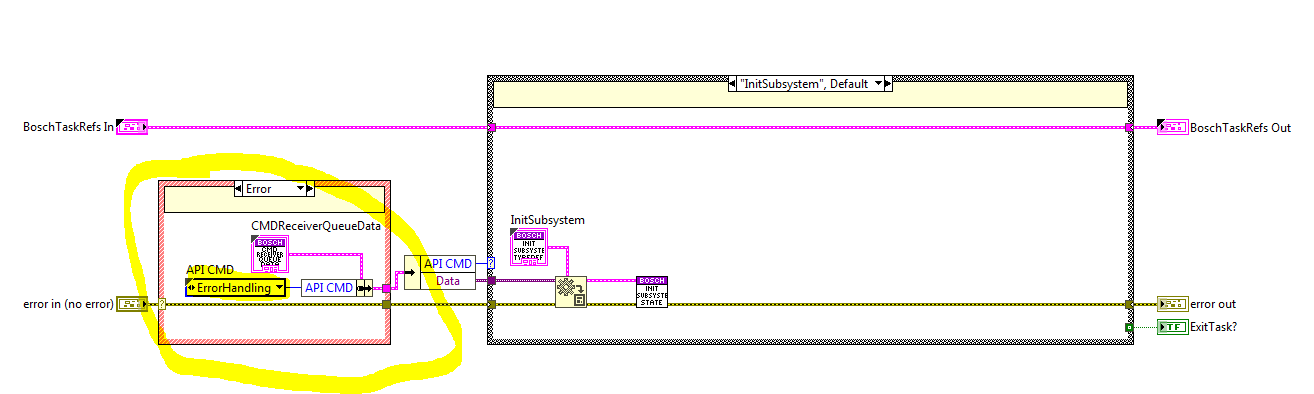
Each of the methods uses this queue to enqueue the next CMD and the CMD receiver loop dequeues the CMDs from the queue at the beginning of each iteration, see figure below. If an error occurred at the previous iteration the ErrorHandling state is executed and the last CMD will be dequeued in the next iteration, see figure below.
Methods¶
The methods of this loop are explained before as public methods of the bosch task.
Task states¶
Here the code for the different task states is explained.
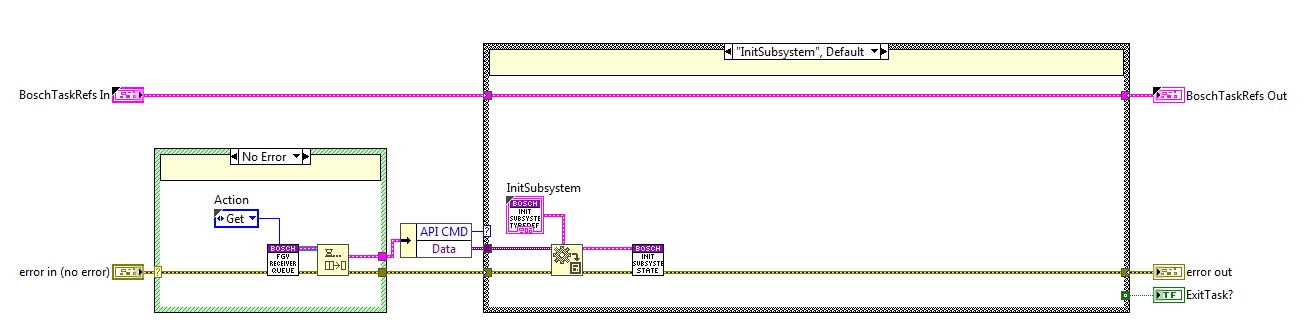
Init Subsystem state¶
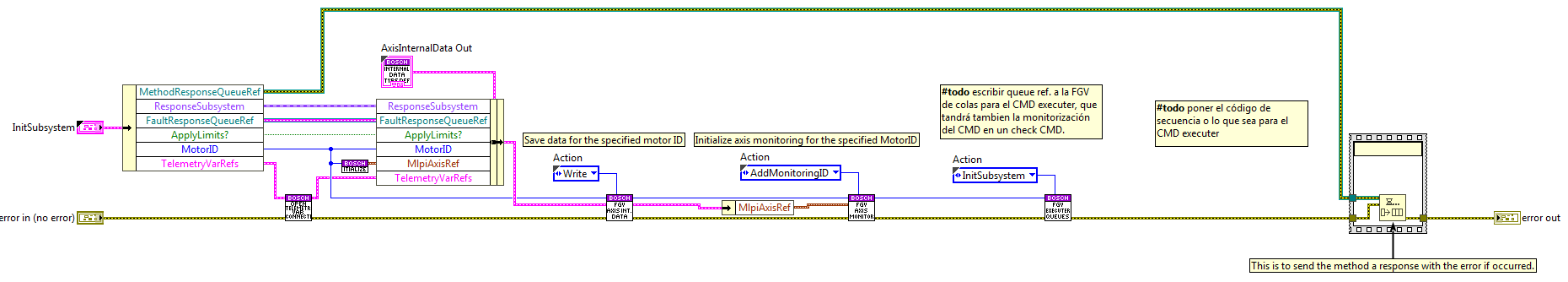
The code here is used when a new subsystem is added, the reference for this subsystem will be the MotorID. To initialize this new system the following actions are executed:
Open the telemetry variable connections.
Save all the subsystem data inside an indexed FGV, “FGV_AxisInternalData”, this FGV is private to ensure that data is only accessed from inside the library.
Save the initialized MLPI axis in another FGV, “FGV_AxisMonitoringIDs”, this FGV is used at the monitoring loop, all the axis here are checked and the data related to it is published at the telemetry vars saved at the FGV_AxisInternalData.
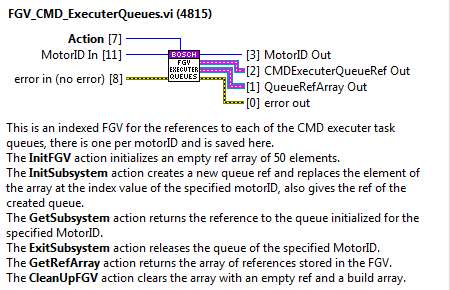
Init the queue for this MotorID, this is done inside another FGV, “FGV_ExecuterQueues”, this FGV saves the queue ref of each initialized motorID. This is done like this to ensure that each system has an independent queue and to enable simultaneous CMDs.
Finally, a response is sent to the calling method, the response is just the error line, this way the calling VI will know if everything was ok while initializing.
Exit Subsystem state¶
The code here is used when an existing subsystem is removed, the reference for this subsystem will be the MotorID. To exit the existing system the following actions are executed:
Open the telemetry variable connections.
Save all the subsystem data inside an indexed FGV, “FGV_AxisInternalData”, this FGV is private to ensure that data is only accessed from inside the library.
Save the initialized MLPI axis in another FGV, “FGV_AxisMonitoringIDs”, this FGV is used at the monitoring loop, all the axis here are checked and the data related to it is published at the telemetry vars saved at the FGV_AxisInternalData.
Init the queue for this MotorID, this is done inside another FGV, “FGV_ExecuterQueues”, this FGV saves the queue ref of each initialized motorID. This is done like this to ensure that each system has an independent queue and to enable simultaneous CMDs.
Finally, a response is sent to the calling method, the response is just the error line, this way the calling VI will know if everything was ok while initializing.
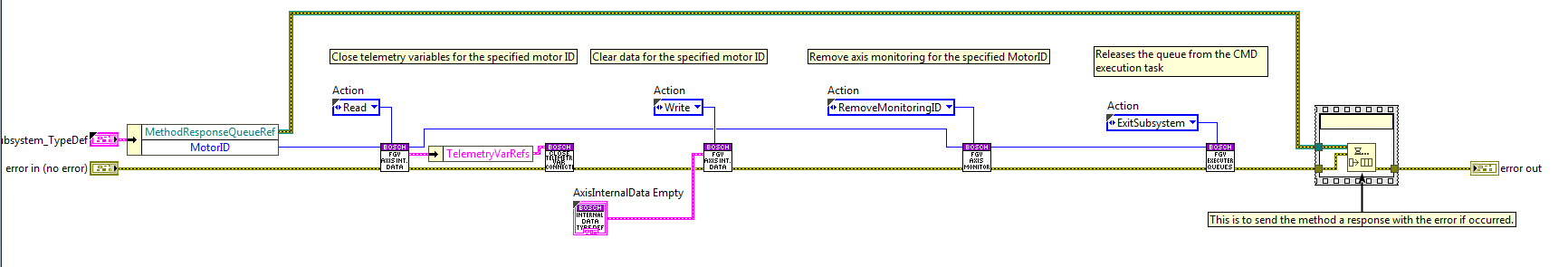
Close Task State¶
Stops the rest of the tasks executed in the bosch task, as well as this one, while closing any open connections.
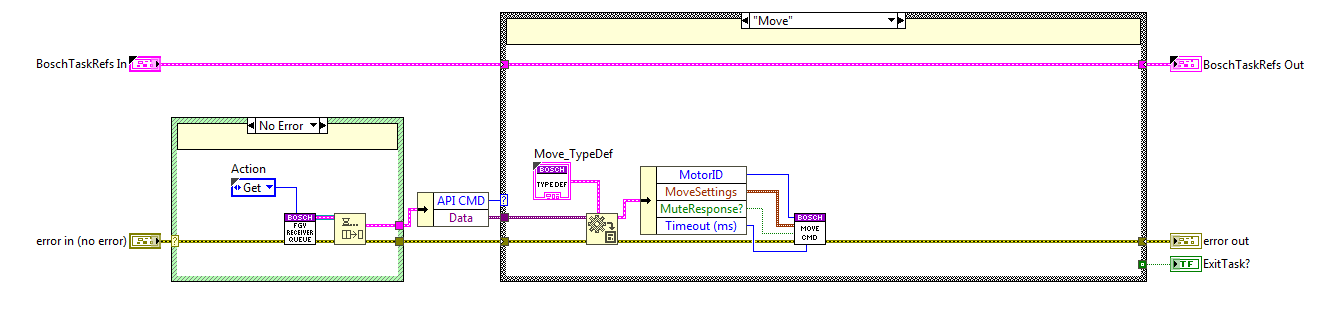
Move State¶
The code is executed when the move method is used, here the MoveCMD private method from the Executer task is called.
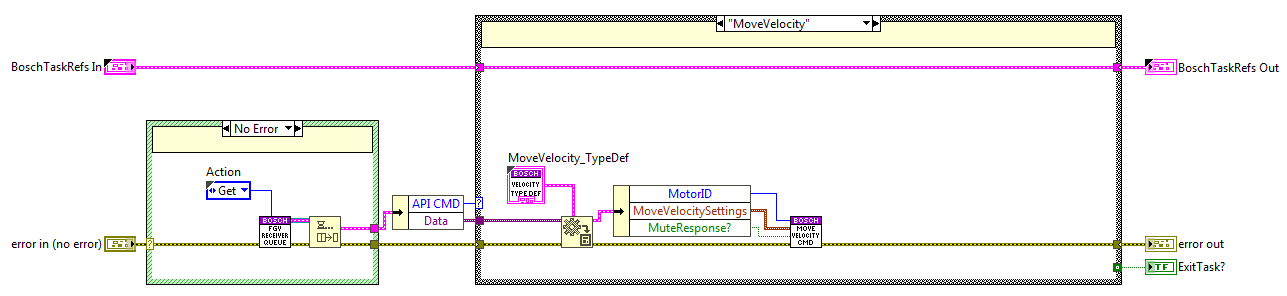
Move Velocity State¶
The code is executed when the moveVelocity method is used, here the MoveVelocityCMD private method from the Executer task is called.
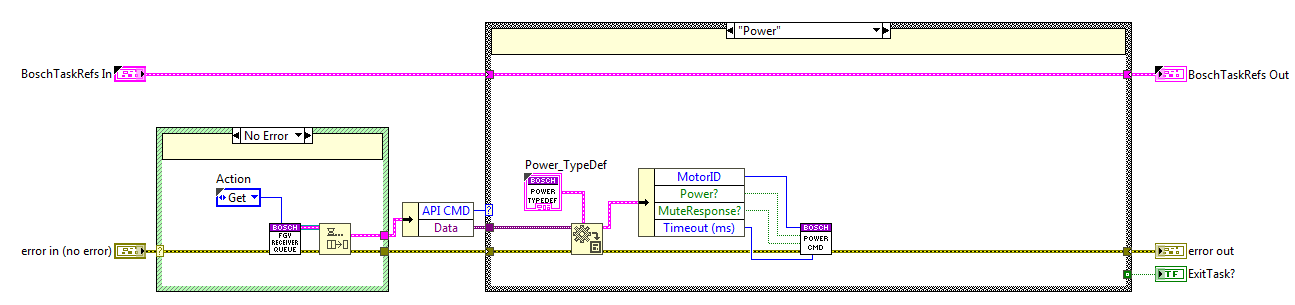
Power State¶
The code is executed when the power method is used, here the PowerCMD private method from the Executer task is called.
Track State¶
The code is executed when the track method is used, here the TrackCMD private method from the Executer task is called.
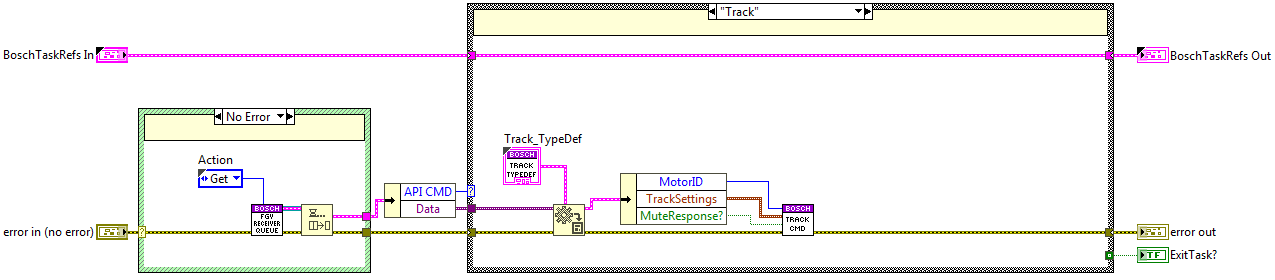
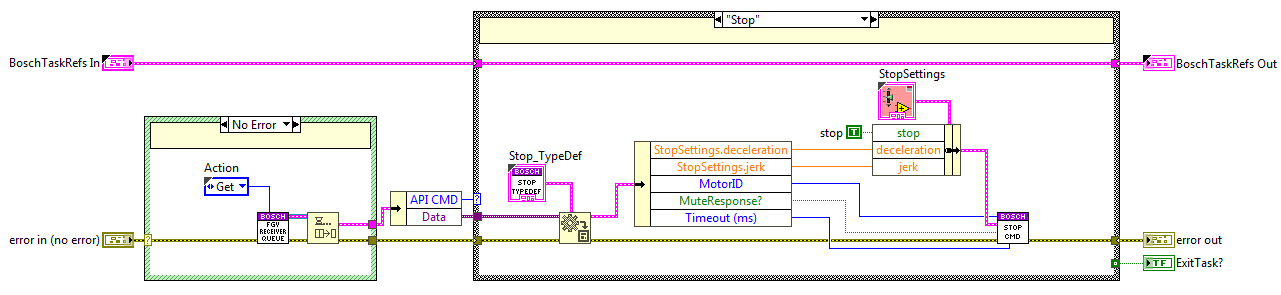
Stop State¶
The code is executed when the stop method is used, here the StopCMD private method from the Executer task is called.
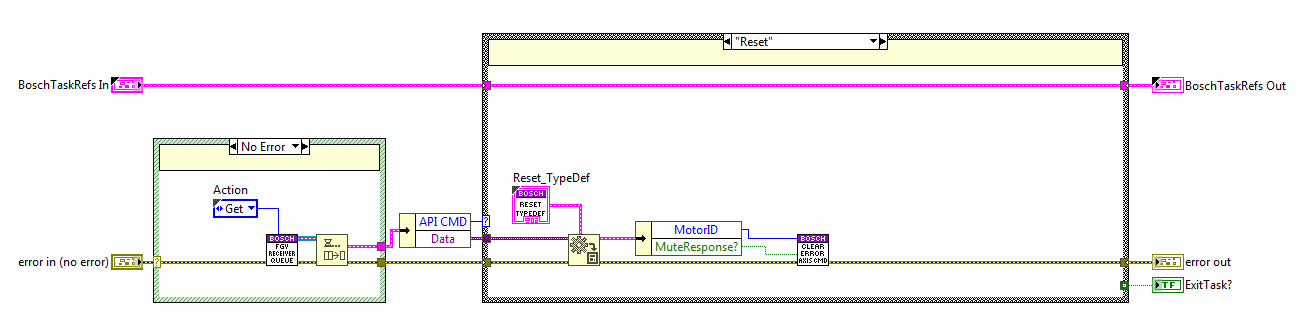
Reset State¶
The code is executed when the reset method is used, here the ResetCMD private method from the Executer task is called.
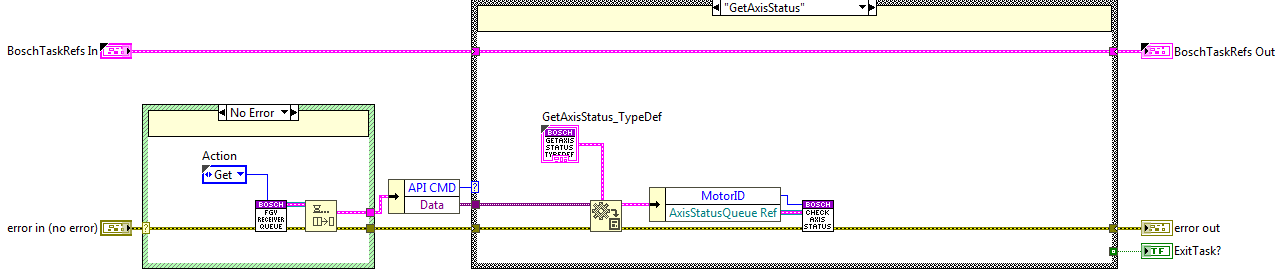
Get Axis Status State¶
The code is executed when the getAxisStatus method is used, here the CheckAxisStatus private method from the Executer task is called.
Error Handling State¶
The code is executed when an error occurs at the error line, here the method from the error task send error is used.
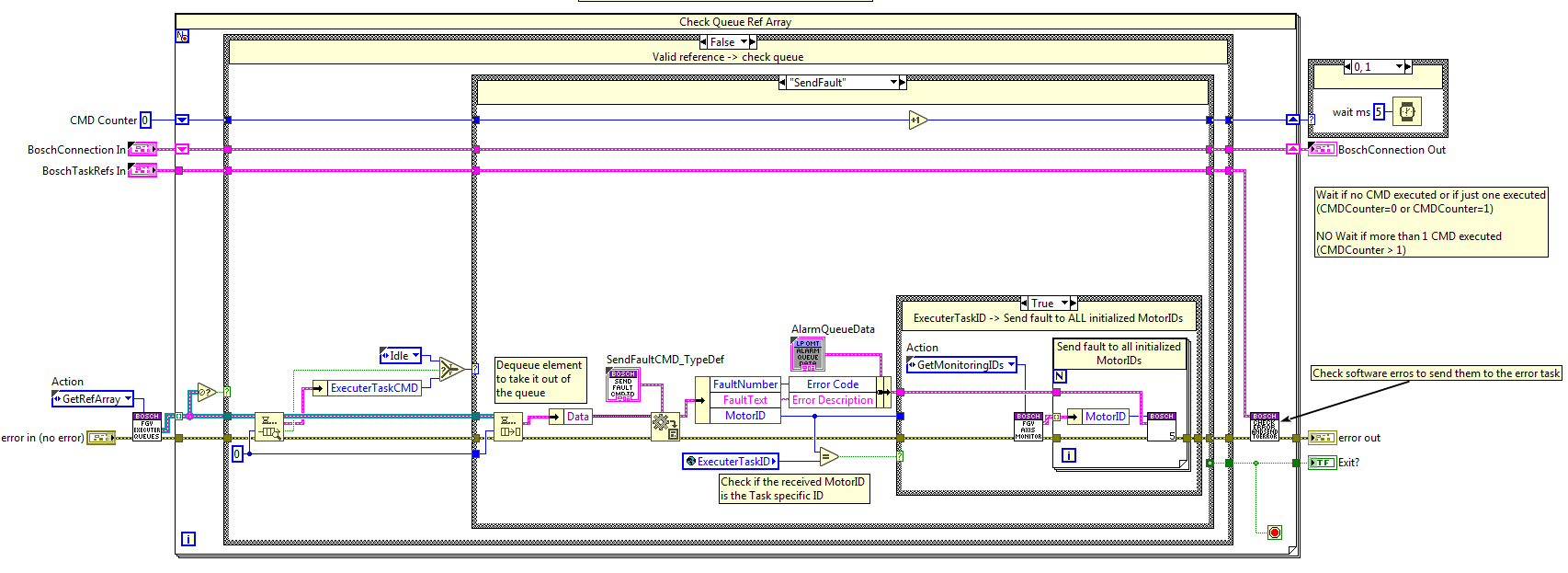
CMD Executer loop¶
This loop receives actions from the CMD receiver and communicates with the Bosch PLC. This loop includes the CMD monitoring, this means that when one CMD takes time to execute a new state is enqueued after sending it to the Bosch system to check the CMDs progress.
Task communication¶
The communication between the methods and the task is not as simple as the one for the CMDReceiver task. Here CMDs must be executed in parallel for more than one MotorID, that’s why there must be more than one queue. To solve this problem and to avoid using lvclasses, that cause problems when deploying to a RT target, the adopted solution is an FGV with a queue array, “FGV_CMD_ExecuterQueues” see Figure 30, each of the queue references of the array is linked to one MotorID. This queue is initialized at the InitSubsystem state of the CMD Receiver task and released at the ExitSubsystem state.
Each of the methods uses the queue related to the specified MotorID to enqueue the next CMD and the CMD executer loop gets all the queues of each iteration. This array is then indexed, and all the queue references are checked for available CMDs.
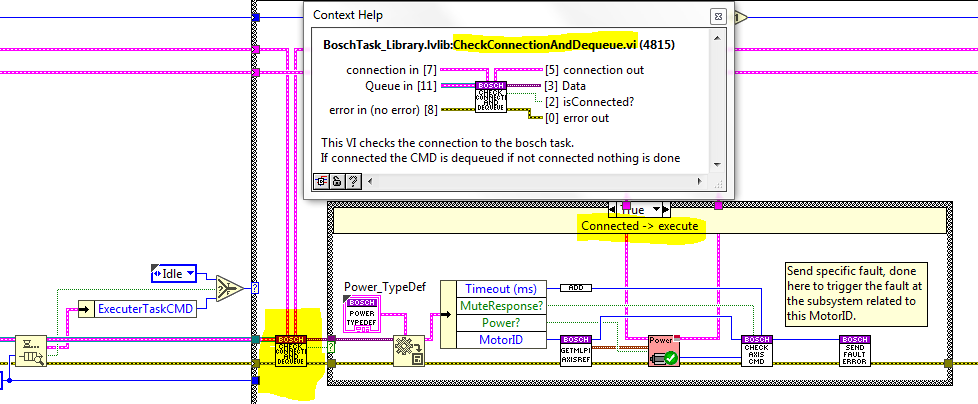
At first the elements in the queue are not dequeued, first the element is previewed. After, at the selected state the required actions are done. Some of the states need to check the connection status before executing the state, see figure below, others do not need to do that and dequeue the queue at the beginning of the state, see figure below.
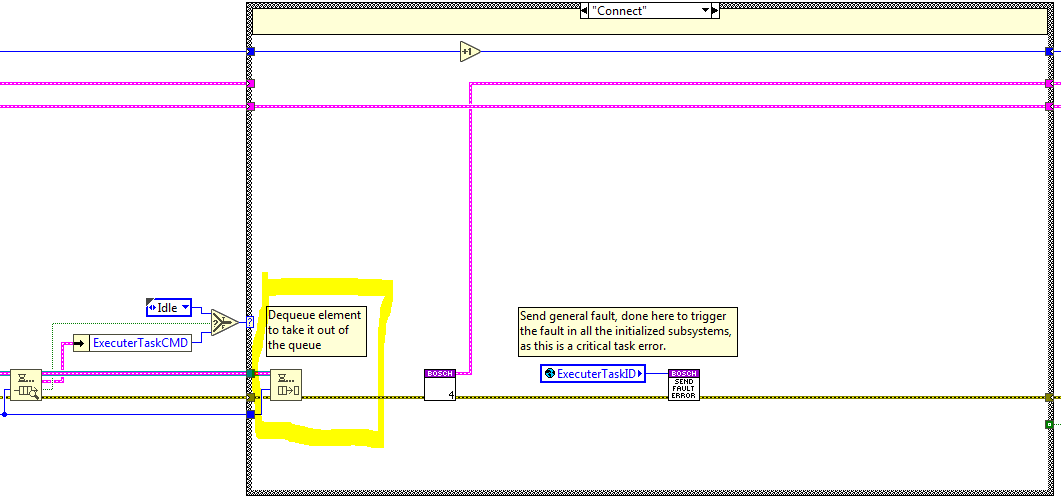
Methods¶
Here the methods of this task are explained. All the methods listed below are private methods that only can be accessed from inside the library.
ConnectCMD¶
Connect task to the Bosch system.
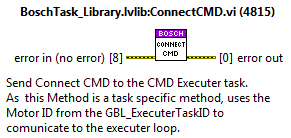
DisconnectCMD¶
Disconnect task from the Bosch system.
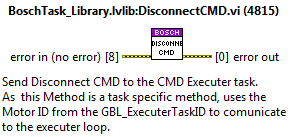
ClearErrorAxisCMD¶
Reset error from the specified MotorID.
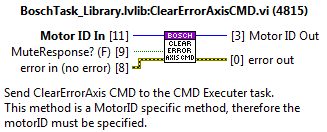
PowerCMD¶
Send power on/off to the specified MotorID.
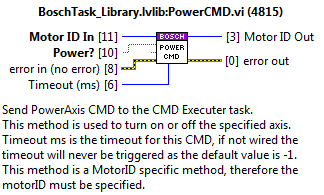
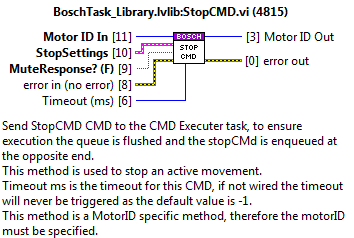
StopCMD¶
send stop to the specified MotorID.
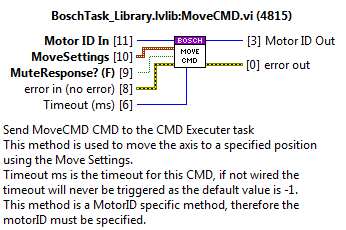
MoveCMD¶
Send move absolute to the specified MotorID.
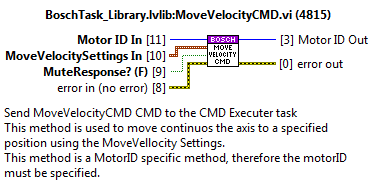
MoveVelocityCMD¶
Send move velocity to the specified MotorID.
Track¶
Send move continuous to the specified MotorID.
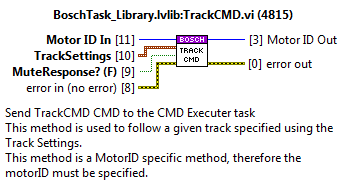
CheckAxisCMD_AtOppositeEnd¶
Checks the specified motionHandle to trigger the statechart when finished or when an error occurs.
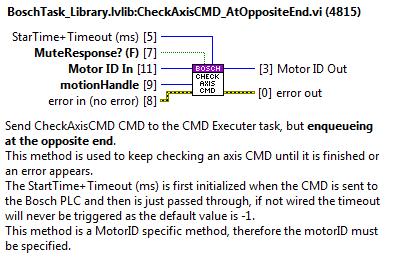
CheckAxisStatus¶
Checks the status of the specified MotorID and answers at the specified AxisStatusQueue.
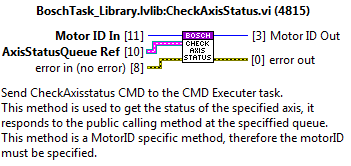
SendDoneCMD¶
Sends the done trigger to the statechart linked to the specified motorID.
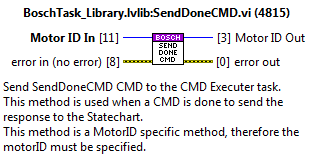
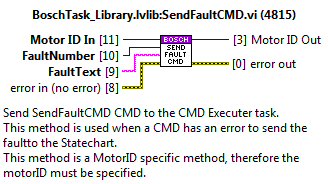
SendFaultCMD¶
Sends the fault trigger to the statechart linked to the specified motorID. Sends the info of the fault to the statechart using the queue ref saved at the FGV_AxisInternalData.
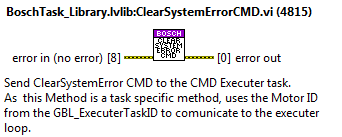
ClearSystemErrorCMD¶
This is a task specific method and is used to clear the general errors of the bosch system.
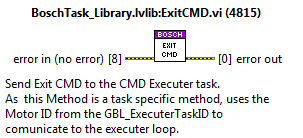
ExitCMD¶
This is a task specific method and is used to close the task.
Task states¶
Here the code for the different task states is explained.
Init¶
Perform the init actions of the task. [Nothing so far.]{.mark}
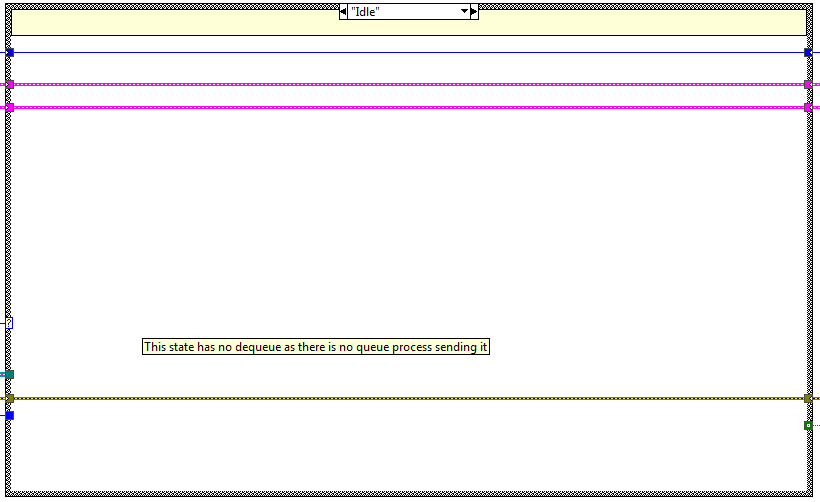
Idle¶
Empty state just to do nothing and wait until another CMD is available.
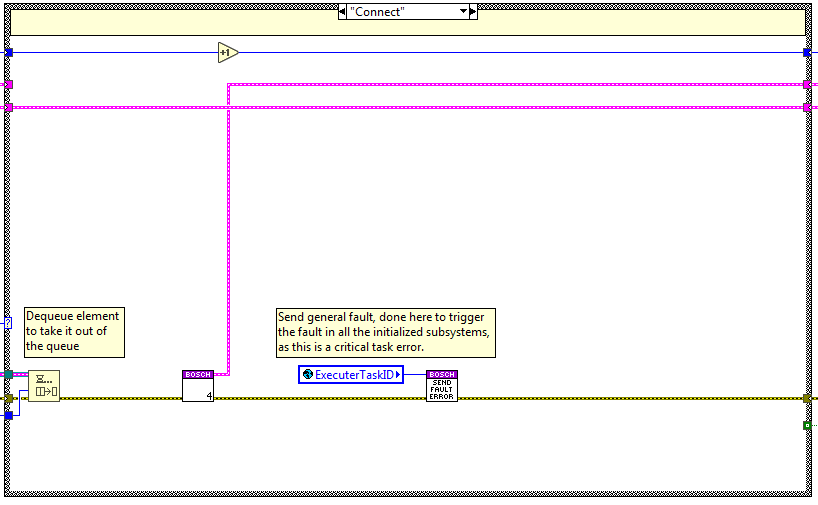
Connect¶
The code is executed when the connect method is used, here the Connection to the Bosch system is done, the connection handle is saved in a FGV (“FGV_BoschConnection”) to access it from the axis monitoring loop.
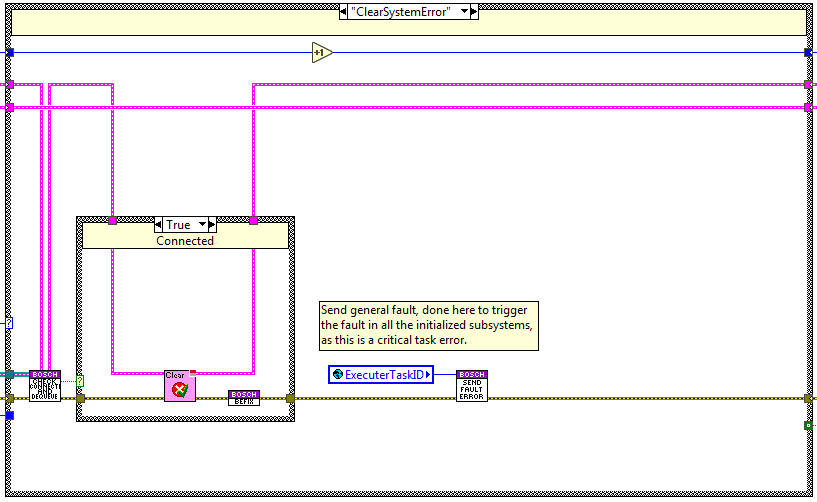
ClearSystemError¶
The code is executed when the clearSystemError method is used, here the function clear error from the Bosch system is done.
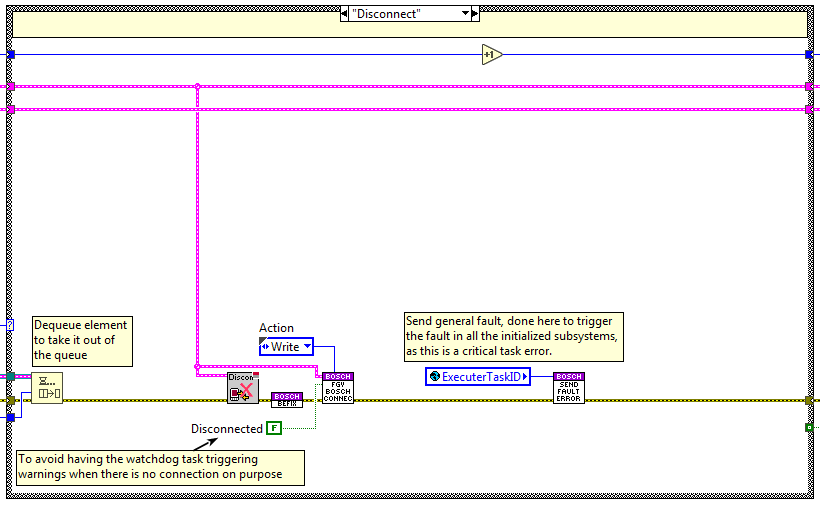
Disconnect¶
The code is executed when the disconnect method is used, here the disconnection from the Bosch system is done, the closed connection handle is saved in a FGV (“FGV_BoschConnection”) to access it from the axis monitoring loop.
ClearError Axis¶
The code is executed when the ClearErrorAxis method is used, here the errors from the axis linked to the specified MotorID are cleared. When done a done response is sent to the statechart related to the MotorID, unless the response is muted.
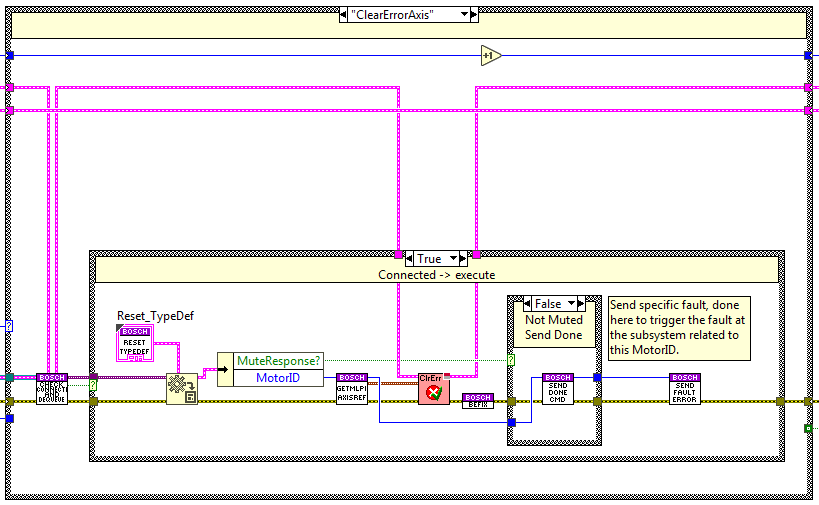
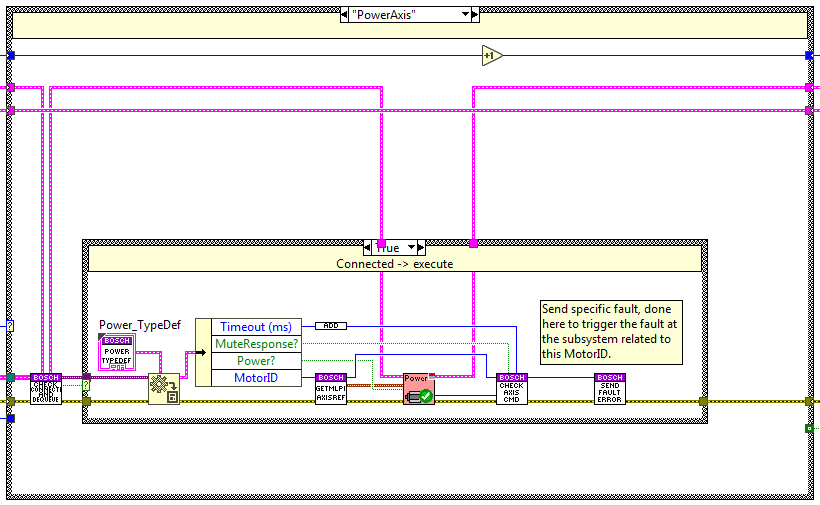
Power Axis¶
The code is executed when the power method is used, here the axis linked to the specified MotorID is powered on or off depending on the specified boolean value. To know when done a new state is enqueued at the opposite end of the queue CheckAxis state, this state checks if the CMD is done, if it has an error and if it was timed out.
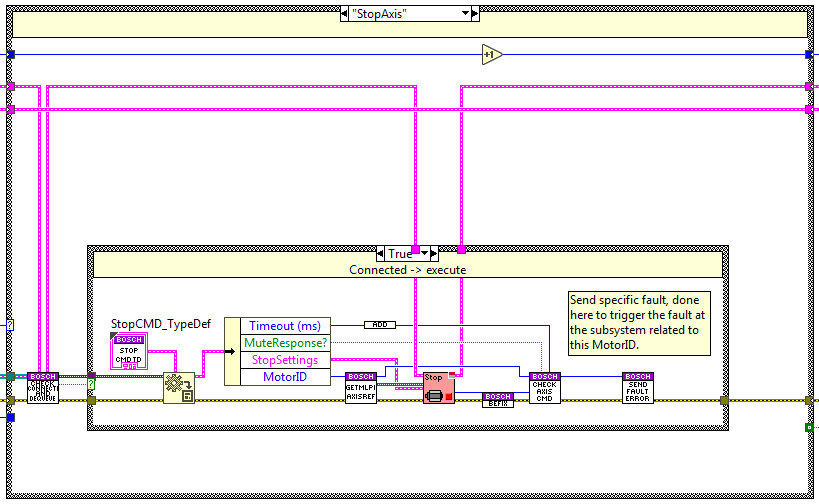
Stop Axis¶
The code is executed when the stop method is used, here the axis linked to the specified MotorID is stopped using the deceleration and jerk specified as settings. To know when done a new state is enqueued at the opposite end of the queue Check Axis state, this state checks if the CMD is done, if it has an error and if it was timed out.
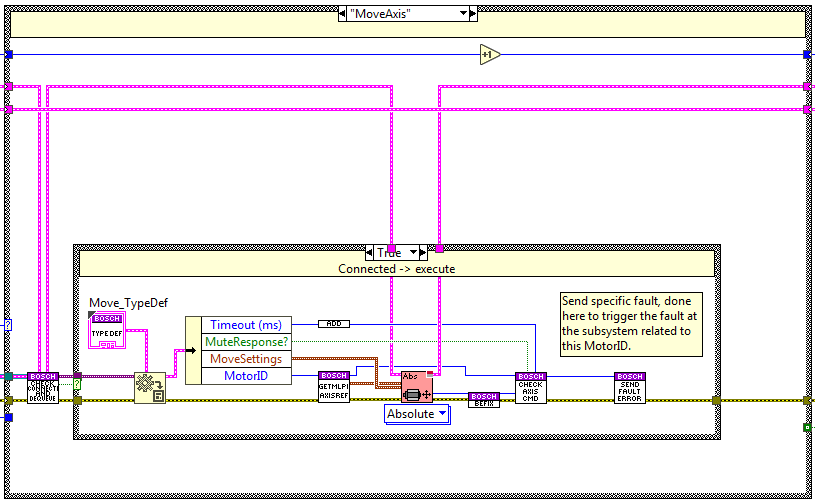
Move Axis¶
The code is executed when the move method is used, here the axis linked to the specified MotorID is moved to the specified absolute position using the acceleration, deceleration and jerk specified as settings. To know when done a new state is enqueued at the opposite end of the queue Check Axis state, this state checks if the CMD is done, if it has an error and if it was timed out.
MoveVelocity Axis¶
The code is executed when the moveVelocity method is used, here the axis linked to the specified MotorID is moved at the specified velocity using the acceleration, deceleration and jerk specified as settings. To know if an error occurs during the move a new state is enqueued at the opposite end of the queue Check Axis state, this state checks if the CMD is done, if it has an error and if it was timed out, but for this specific CMD the only important check is the error check, as a move velocity can´t have a done or a timeout.
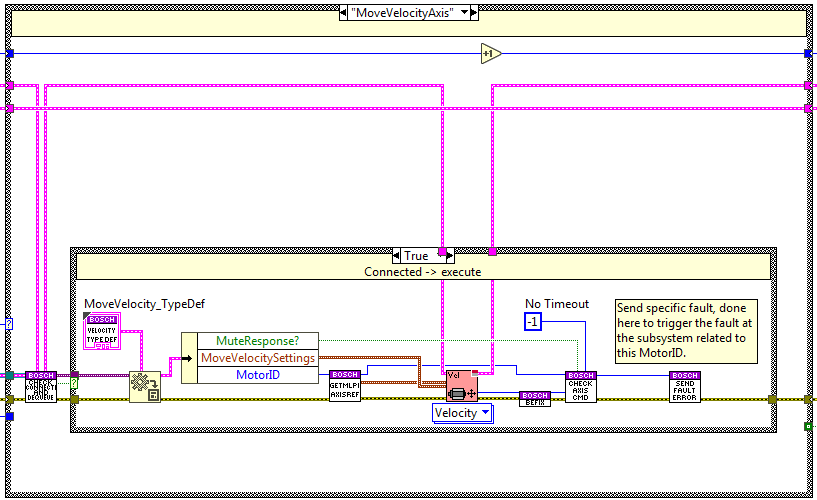
Track Axis¶
The code is executed when the track method is used, here the axis linked to the specified MotorID is moved to the specified position using the endSpeed, acceleration, deceleration and jerk specified as settings. To know if an error occurs during the move a new state is enqueued at the opposite end of the queue Check Axis state, this state checks if the CMD is done, if it has an error and if it was timed out, but for this specific CMD the only important check is the error check, as a track can´t have a done or a timeout.
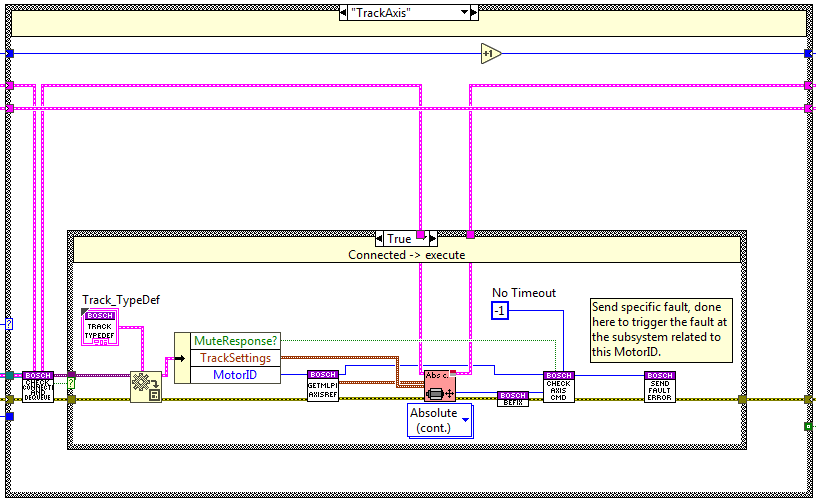
CheckAxisCMD¶
This state checks the CMD status, this means that it checks if the CMD is done, if it has an error and if it was timed out.
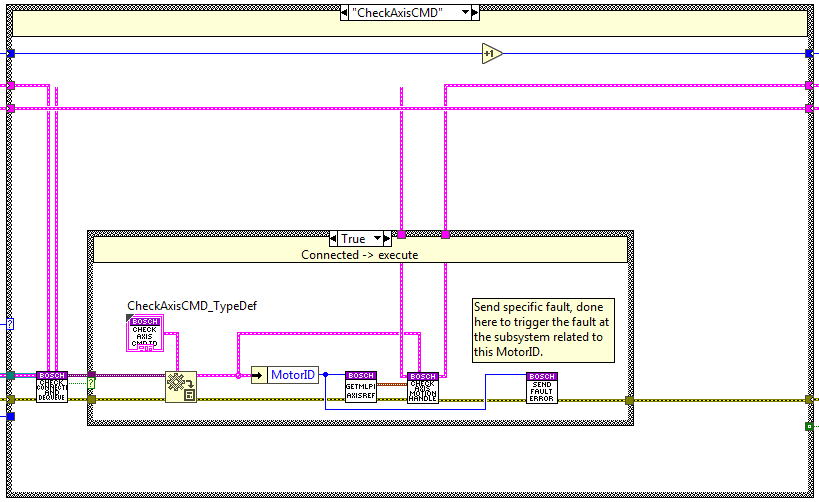
Exit¶
This case is used to exit the task, here is checked that the calling method is the task exclusive MotorID that is the 0.
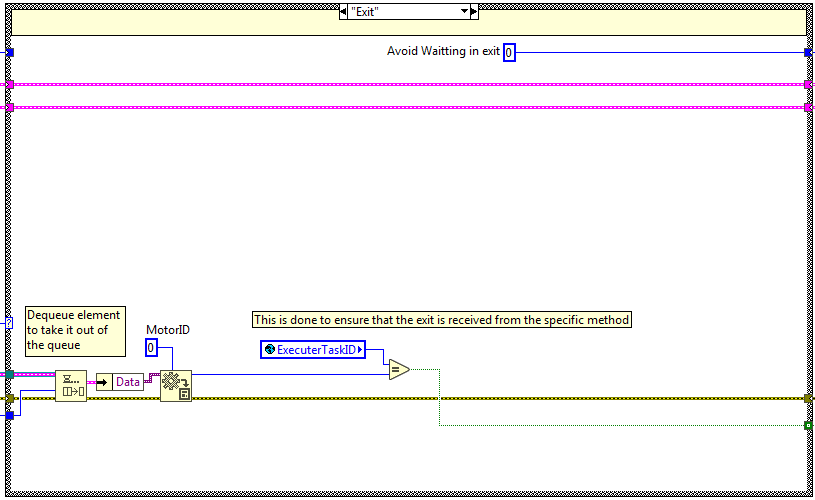
Send Done¶
The code is executed when the send done method is used, here a done trigger is sent to the statechart linked to the specified MotorID.
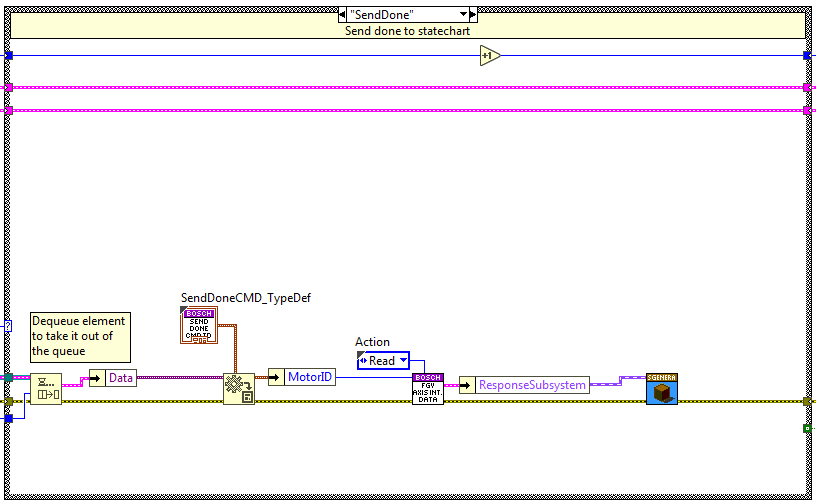
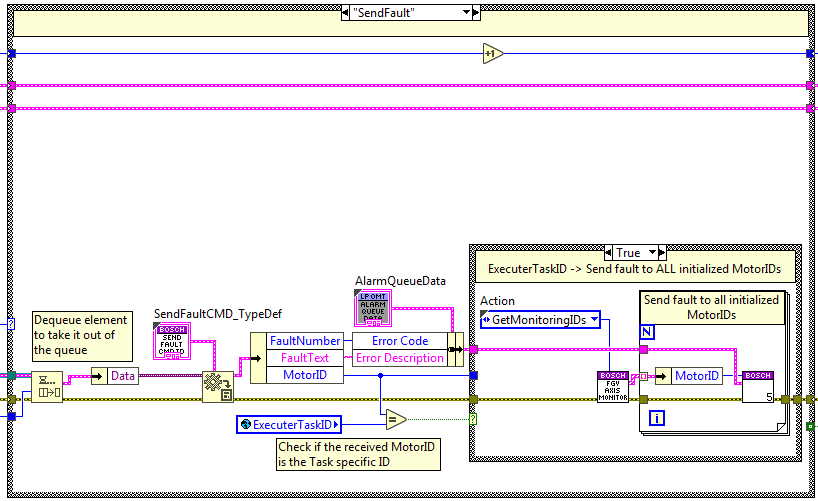
Send Fault¶
The code is executed when the send fault method is used, here a fault trigger is sent to the statechart and the faultResponseQueue is updated with the fault information linked to the specified MotorID.
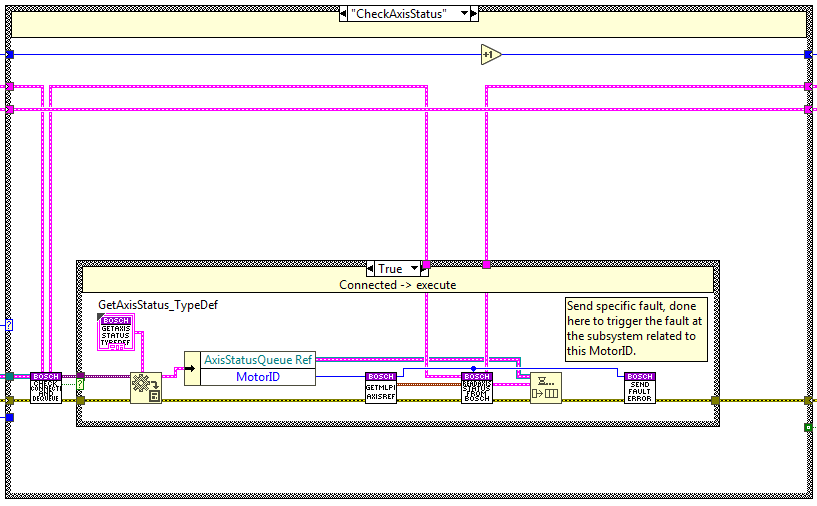
Check Axis Status¶
The code is executed when the check axis status method is used, here the status of the axis linked to the specified
MotorID is checked and updated in the response queue called AxisStatusQueue re, this queue is dequeued at the calling
public method GetAxisStatus.
Axis Monitoring task¶
This task is divided in two loops, one for the axis values (position, velocity, acceleration, torque and status) and the other loop is used to read the limits status (positive and negative limit switch). This is done like this, due to the delay when reading the limits.
Axis values monitoring loop¶
This loop publishes the telemetry given by the GetAxisValues function from the MLPI library, this function returns: actual position, actual velocity, actual acceleration, actual torque, state, state extended, diagnosis number and condition. From all this data the wanted one is only published, to do so at the initSubsystem the wanted variables must be specified, if no variable is specified that value is not published.
The telemetry vars published here are opened at the InitSubsystem state of the CMD Receiver and closed at the ExitSubsystem state.
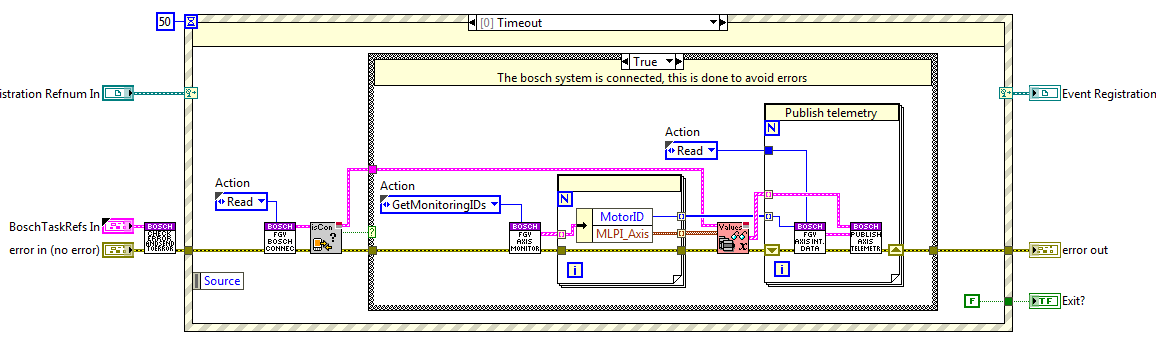
Task communication¶
This task has no communication, this task is checking if the connection is established to the bosch system and if done the initialized subsystems variables are published constantly.
The only communication is the stop event launched from the CMD receiver Close task state.
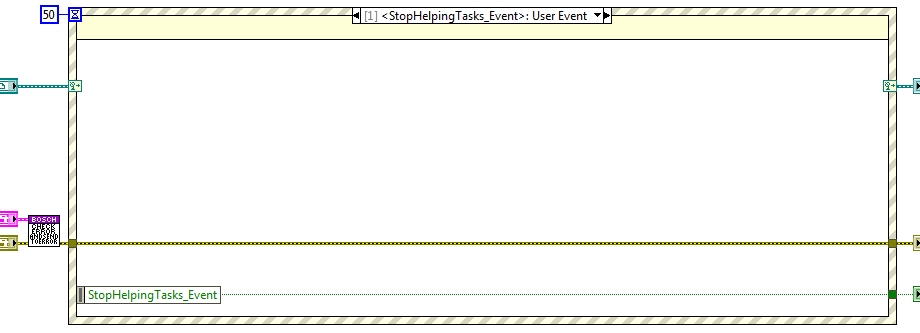
Publishing vars¶
Here the variables that the system can publish are shown.
Position var ref. DBL array type var.
Velocity var ref. DBL array type var.
Status var ref. String type var.
Status code var ref. I32 type var.
Torque var ref. DBL array type var.
Acceleration var ref. DBL array type var.
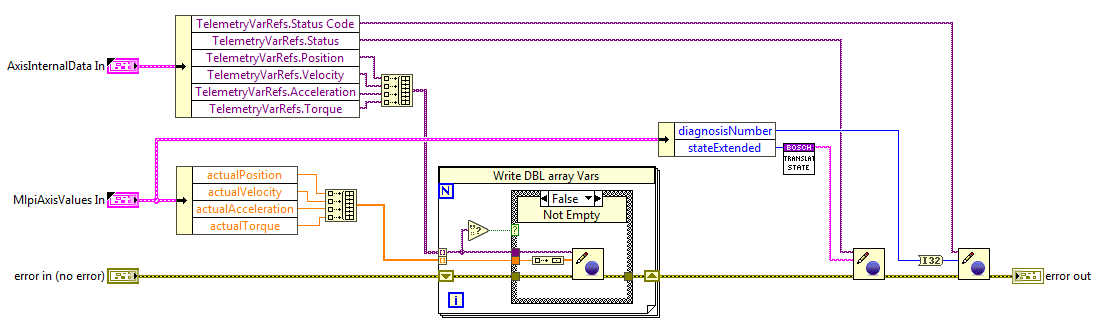
Limits monitoring loop¶
This loop publishes the status of each axis limits, the values for are given by the ReadDataULong function from the MLPI library, this function returns the value of the specified parameter. This code is executed for all axis that have the apply limit control to true when initialized.
The telemetry vars published here are opened at the InitSubsystem state of the CMD Receiver and closed at the ExitSubsystem state.
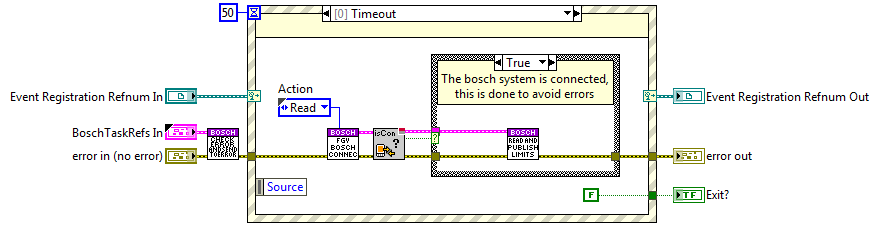
Task communication¶
This task has no communication, this task is checking if the connection is established to the bosch system and if done the initialized subsystems variables are published constantly.
The only communication is the stop event launched from the CMD receiver Close task state.

Publishing vars¶
Here the variables that the system can publish are shown.
Positive Limit var ref. Boolean type var.
Negative Limit var ref. Boolean type var.
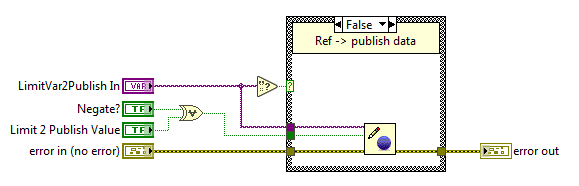
Watchdog¶
This task monitors the connection between the PXI and the Bosch PLC, if the connection fails several times an alarm is triggered. Additionally, this task publishes the status of the connection and the bosch controller state (possible controller estates are: BB, P0, P1, P2 and P3).
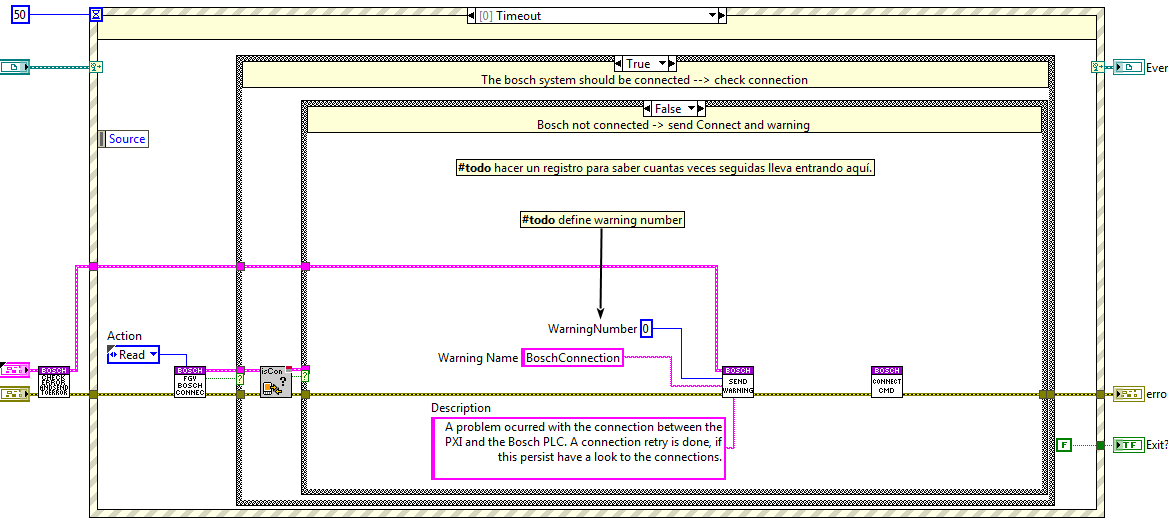
Task communication¶
This task has no communication, this task is checking if the connection is working between the bosch system and the PXI, if okay nothing is done, but if not working a warning is sent.
The only communication is the stop event launched from the CMD receiver Close task state.

Error task¶
This task publishes the software errors and warnings related to the Bosch task.
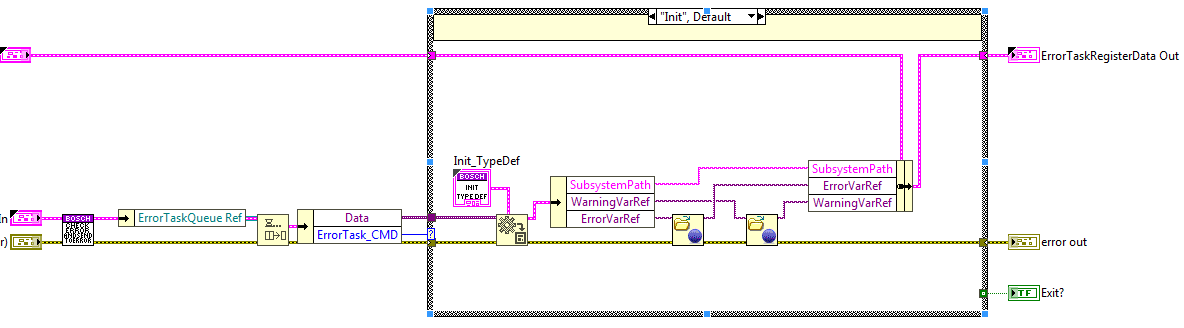
Task communication¶
This task has a single queue and the methods use it to publish the available states, these methods are private methods. The queue reference is created at the InitActions and released at the ExitActions of the bosch task. The reference is saved to a cluster, “BoschTaskRefs”, as it has no need to be used out of the library main VI.
Methods¶
The methods available for this task are described in the upcoming sections.
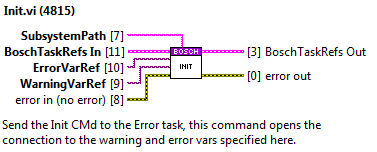
Init¶
This method enqueues the init state of the error task.
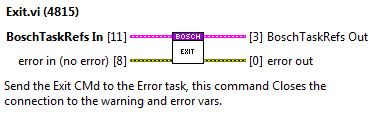
Exit¶
This method enqueues the exit state of the error task.
Send Error¶
This method enqueues the send error state of the error task and sends the error cluster wired to the Error2Send as CMD data.
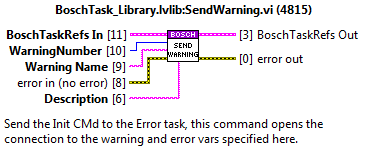
Send Warning¶
This method enqueues the send warning state of the error task and sends the Waring number, warning name and description as CMD data.