11. Virtual Machines¶
Virtual Machines were created to speed the process of TMA Software deployment. It enables a developer to interact with the TMA software on their personal work machine, usualy with limited functionality. Here you can find the different TMA Software containers that are available along with detailed instructions on how to deploy them.
11.1. Windows10¶
The Windows 10 Virtual Machine is required by the MCC to run the EUI. This is because the EUI must first connect to the NSV’s before allowing any user logins. This Virtual Machine is also able to run a variety of simulators.
11.1.1. Pre-requisites¶
- Install Oracle VM VirtualBox
- Install Oracle VM VirtualBox Extension Pack
- Figure out that the subnet IP address of your host machine. My machine was in the subnet
192.168.1.95so this is what I will use in these steps. The IP address used in these steps MUST be in your subnet, otherwise this windows 10 machine will be unreachable. A user who reviewed this work for example had to use the IP address of192.168.0.123.
11.1.2. NSV Simulator¶
The NSV Simulator is required to be able to run the EUI. This is a useful simulator when you wish to verify that the EUI is installed and is able to communicate to the NSV’s
- Connect to the PDM server, instructions for Accessing La Serena PDM Server here.
- Download the tma_windows10 Virtualmachine TSS-Share/TMA/tma_windows10.ova.
- Open VirtualBox and import the machine, verify that the second network is a bridged adapter.

- Start the virtualmachine and set the IP address of the second network to be
195.168.1.95with subnet255.255.255.0
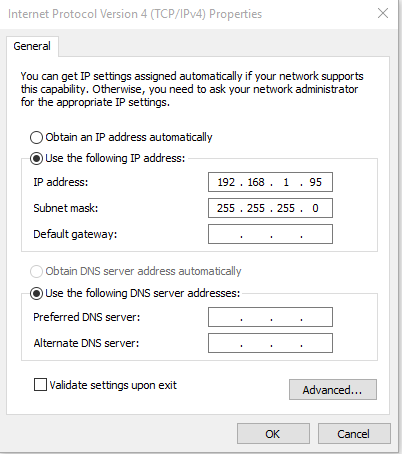
- Once inside the Windows10 Virtual Machine open the NI Distributed System Manager. There should be an icon for the program on the Desktop.
- If you do not see the image below restart the machine, for a reason I do not know the VM has mal booted preventing NSV’s from becoming available.
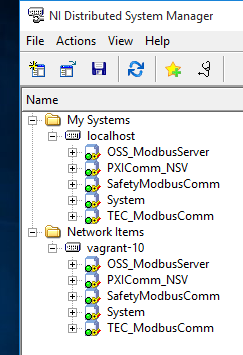
- Double click the program
ATSSimulatorsAndTools/SimulateTelemetry/SimulateTelemetry.exethis program is writing random values to the NSV’s. - Open the NI Distributed System Manager. Expand one of the items under
localhost. You should see these values changing at random. We have now demonstrated that the NSV simulator is functioning properly. We verify the values are indeed deployed and being changed via the NI Distributed System Manger.
11.1.3. TMA & Axes Simulator¶
The TMA and Axes PXI Simulator is capable of responding to commands sent to it. This is a quick way of verifying changes made to the commanding component, or in other words the MTMount CSC (or in legacy software, the Operation Manager).
- Connect to the PDM server by following the instructions here Accessing La Serena PDM Server
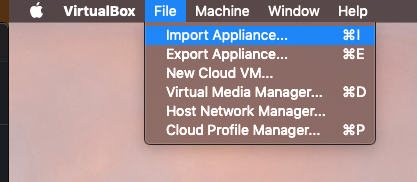
- Download the file
TSS-Share/TMA/VM_AxesPXI.ova - Download the file
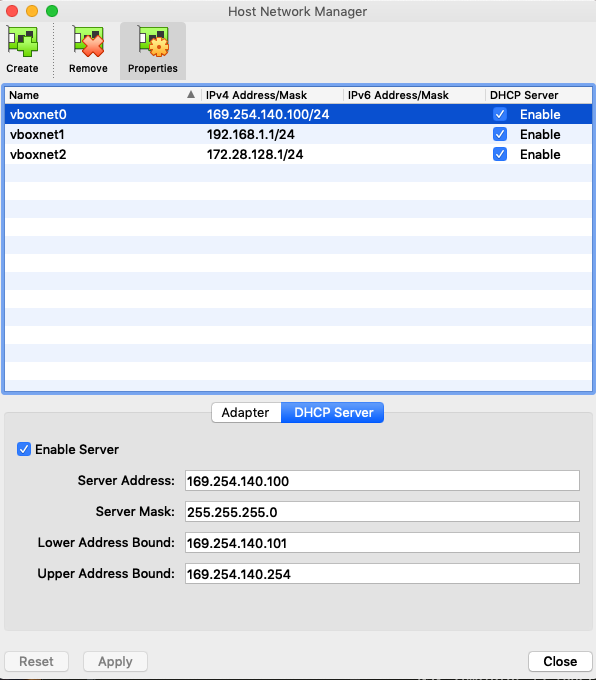
TSS-Share/TMA/VM_TMA-PXI.ova - Open Virtual box and navigate to “Host Network Manager”
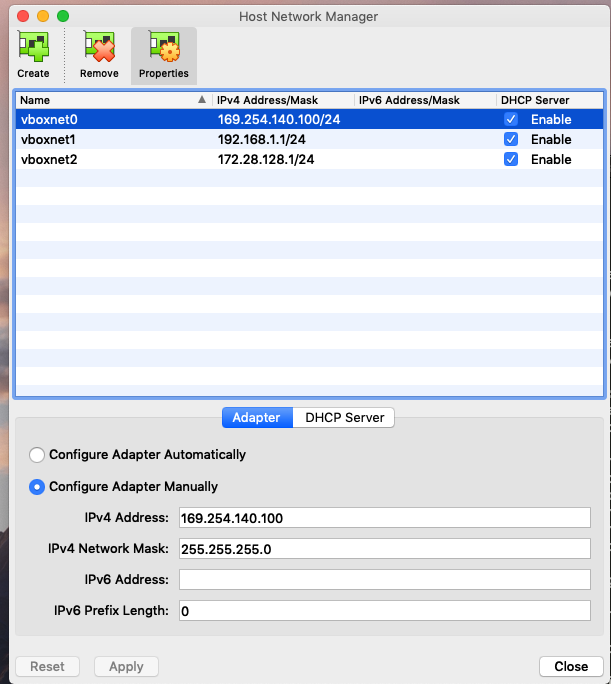
- Create a Host-only adapter using the configuration shown in the two images below, you will need only vboxnet0.
- Import the VM_Axes.PXI.ova file.
- Select “Generate new MAC addresses for all network adapters” and import the Virtualmachine.

- Ensure that under Network settings the virtual machine is using the Host Only adapter that we created.
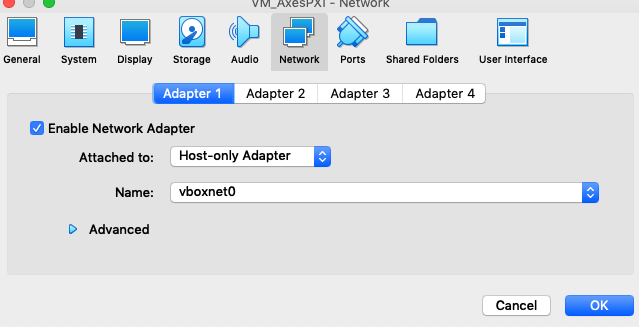
- The Virtualmachine should now be able to boot up and obtain an IP address within the range that we specified when configuring the Host only adapter
11.2. CentOS¶
A CentOS container is capable of dupliating the Mount Control Computer (MCC). The MCC can run the Engineering User Interface (EUI) which allows controlling of the telescope. The MCC is also the first interact with the Software Abstraction Layer (SAL). Here we will go through the process of deploying a CentOS Docker container.
11.2.1. Pre-requisites¶
Most of the TMA Software is LabVIEW. LabVIEW is a window intensive software and as a result requires that you install some method for viewing windows from your Docker container.
- Install Docker
- Install an X Windows Server
- Complete the steps for Accessing Nexus Repo
- Complete the steps for NSV Simulator. Note down what IP address was used for this step, you will need it later to complete this setup. Have these NSV’s running otherwise the EUI will not be able to run. This is because on startup the EUI is looking for the NSV’s. You will see dialogues complaining that it is unable to find certain values with a given IP address that you must configure.
11.2.2. EUI (Engineering User Interface)¶
The EUI controls the TMA. It can determine if the EUI itself is in control, if the CSC is in control, or if the Hand Held Device is in control.
- Do a global search and replace for
HMIComputers/Configuration/HMIConfig.xmlandHMIComputers/Configuration/HMITelemetryVariablesURLs.ini. The value you are searching for is192.168.1.95and you are replacing this with the same IP address that you wrote down in the pre-requisite of this task. - Pull the Docker container
docker pull ts-dockerhub.lsst.org/tma_software:develop - Run the Docker container using the proper arguments to run the Windows X server. Mine for example is
docker run -it -e DISPLAY=$IP:0 -v /tmp/.x11-unix:/tmp/.x11-unix -v /Users/aheyer/gitdir/:/home/saluser/gitdir andrewheyer/tma_software:develop
The command which worked for a linux user is sudo docker run -it --net=host --env="DISPLAY" --volume="$HOME/.Xauthority:/root/.Xauthority:rw" -v /home/rfactory/lsst/docker/:/home/saluser/gitdir ts-dockerhub.lsst.org/tma_software:develop
- Do
labview64 - When asked to “Select files to recover” deselect all and Discard.
- Open the
LSST_HMIs.lvprojfile. It should already be listed under “All Recent Files” - When asked to find “FGV_BasicFGVAction.ctl” open the drop down selection from the top. The last item from this drop down menu will have a path ending with “/_controles”, open this path. You will see the
FGV_BasicFGVAction.ctlfile here. Double click it. - Ignore the “Load Warning Summary” Dialogue.
- The Labview project should now be open, expand “Main” and double click “HMIMain_EUI.VI”
- A “Resolve Load Conflict” window will appear, double click the middle option. This option also is the only one that has a “14.0” string under “LabVIEW Version”. Double click this option.
- Ignore the “Load Warning Summary” Dialogue.
- Click the run arrow.
- Login user=MUser pw=1234
- Once logged in we have demonstrated that the EUI is able to communicate to the NSV’s. The most simplistic way to generate NSV’s is by running the NSV Simulator on a Windows 10 Machine.